A Comprehensive Local Testing Stack to Hone Your Skills
Among the many tools released in recent years, a robust local environment for testing and experimentation has remained surprisingly elusive. This post introduces a brand-new local testing stack that’s both easy to run and advanced enough to challenge testers of all skill levels.
One frequent struggle for testers is finding an application that’s complex enough to simulate real-world conditions yet not too cumbersome to set up. This local testing stack addresses exactly that need—giving you real services, real dependencies, and a variety of features, all configured to run locally via Docker Compose.
All code is available online for inspection:
Why Use This Local Testing Stack?
Many testing demonstrations rely on trivial examples that don’t mirror genuine production complexities. In contrast, this stack provides:
- Simple Setup: Just a couple of Docker commands, and you have a fully functioning environment.
- Multiple Services: A React-based frontend, a Spring Boot backend, a message broker, a local language-model-based assistant, monitoring tools, and more.
- Realistic Features: User authentication, role-based access, product management, data persistence, asynchronous events, and real-time monitoring.
- Test-Focused Design: Plenty of endpoints, concurrency possibilities, and advanced flows that let you practice functional, security, performance, and exploratory testing.
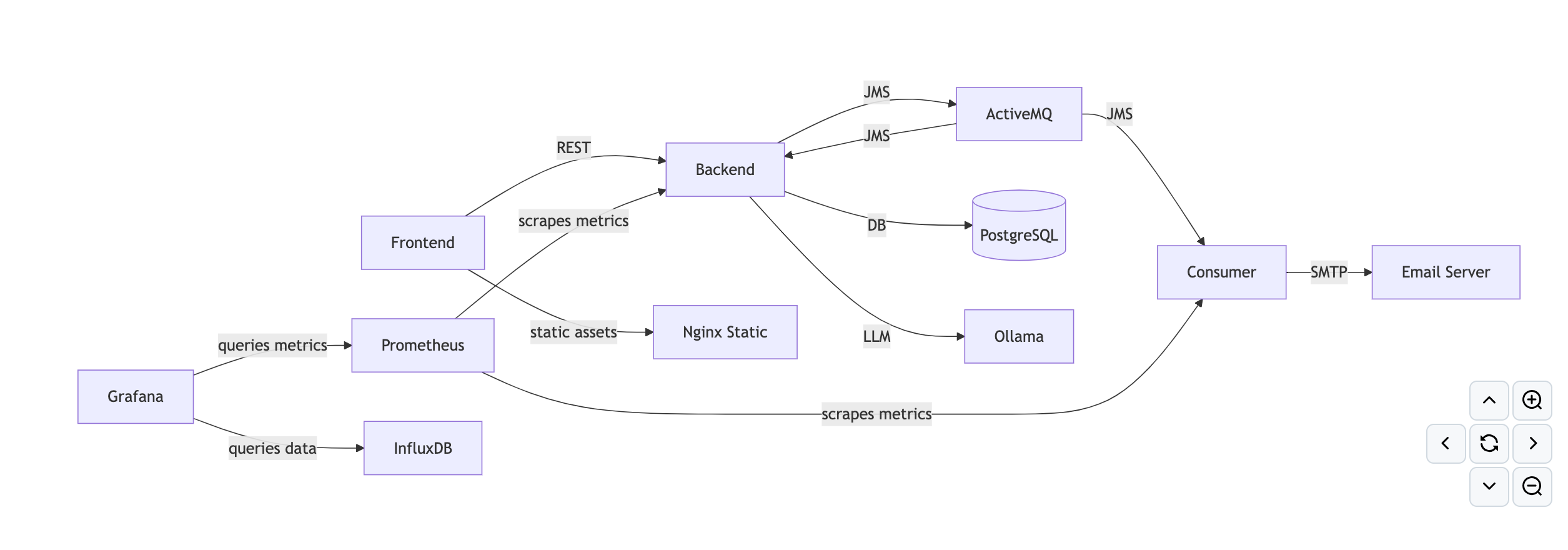
Architecture Overview
The architecture consists of several key components working together:
Key Components:
- Backend: Spring Boot with JWT authentication, PostgreSQL, and ActiveMQ integration.
- Frontend: React + Vite for fast builds and a modern UI.
- Email & Messaging: ActiveMQ for asynchronous tasks, MailHog for email capture.
- Monitoring: Prometheus & Grafana for performance metrics, plus a WebSocket-based traffic monitor for real-time request logs.
- Local LLM Server: Explore language-model-based suggestions or text generation without external dependencies.
- Nginx: Serves static assets, emulating a lightweight CDN.
Major Features
Below is a quick tour of the built-in features you can test right away:
Product Management
- View, Add, Edit, and Delete products in the system.
- Designed to test CRUD endpoints, concurrency, and validation scenarios.
User Management
- Control user roles (Admin vs. Client) and handle sign-up and sign-in flows.
- Perfect for testing role-based access control and JWT token handling.
Order Processing & Profile
- Place orders, track statuses, manage your profile info, and review order history.
- Exercises cart logic, inventory updates, and state transitions in a realistic setting.
Advanced Monitoring: Traffic Monitor
- A WebSocket-based tool that streams all HTTP requests and responses in real time.
- Ideal for immediate debugging, performance checks, or concurrency validation.
LLM Integration
- LLM Assistant: A local text generator that streams responses via Server-Sent Events (SSE).
- Test how prompts and conversation flows are handled in real time—no external calls required.
Utilities
- QR Code Generator: Generate scannable QR codes for any text or URL.
- Email Service: Submit emails asynchronously and see them delivered after a short delay in MailHog.
Each feature is substantial enough to challenge testers, providing ample opportunities to practice scenario testing, negative testing, security checks, performance runs, and more.
Quick Start Guide
Clone the Repository
Access the code here: awesome-localstack
Spin Up the Full Stack
docker compose up
All containers—backend, frontend, database, broker, monitoring, local language-model service, etc.—will start.
Check Your Services
- Backend: http://localhost:4001/swagger-ui/index.html
- Frontend: http://localhost:8081/login
- Prometheus: http://localhost:9090/
- Grafana: http://localhost:3000/login (admin/grafana)
- ActiveMQ: http://localhost:8161/
- MailHog: http://localhost:8025/
- Local LLM Server: http://localhost:11434/api/tags
Spin Up the Lightweight Stack
docker compose -f lightweight-docker-compose.yml up
Check Your Services
- Backend: http://localhost:4001/swagger-ui/index.html
- Frontend: http://localhost:8081/login
Start Exploring
- Log in with admin or client credentials.
- Try product management flows, experiment with sending emails, or watch the traffic monitor to see every request.
Why Testers Should Embrace This Stack
- Realistic Complexity: Databases, messaging queues, authentication, and concurrency can all be tested in a single environment.
- Ease of Deployment: Start and stop all services with Docker—no separate installs needed.
- Built-In Observability: Track performance and request logs in real time, enabling a deeper understanding of system behavior.
- Safe Environment: Experiment freely without risking production incidents or incurring external API costs.
Potential Test Strategies
Here are a few ways you can leverage this stack for testing:
Authentication & Authorization
- Validate role restrictions. Confirm that unauthorized users can’t access admin-specific endpoints.
- Verify token generation, refresh flows, and expiration edge cases.
Performance & Load
- Use k6 (or similar) to generate traffic.
- Monitor metrics in Prometheus/Grafana. Observe concurrency handling in the traffic monitor.
Security Checks
- Look for potential SQL injection or XSS vulnerabilities.
- Attempt unauthorized data access using forged or tampered tokens.
Messaging & Asynchronous Flows
- Place multiple orders quickly to test queue handling in ActiveMQ.
- Inspect MailHog to ensure no email is lost under load or concurrency.
Real-Time Monitoring
- Combine the traffic monitor’s immediate feedback with conventional logs.
- Debug and isolate issues faster by pairing request details with backend logs.
Challenging Questions for Testers
- How does the system behave under concurrency when multiple users attempt to update the same product simultaneously?
- Check for race conditions, locked tables, or inconsistent data states in the database.
- What happens to email requests if ActiveMQ becomes overloaded or temporarily unavailable?
- Will the system retry, queue them up, or fail immediately?
- Are you able to break or exceed any parameter limits in the product creation endpoints?
- Consider boundary testing for name, price, and quantity.
- Can you identify areas where load testing reveals performance bottlenecks?
- Use the real-time traffic monitor and Prometheus metrics to pinpoint slow endpoints or resource contention.
- What does the local language model assistant do if provided with a particularly large or malformed prompt?
- Does the system degrade gracefully or show any unexpected failures?
Conclusion
This local testing stack offers a comprehensive setup to practice and refine your testing strategies. Whether you’re exploring security, performance, or everyday functional testing, you’ll find plenty of scenarios that mimic real-world challenges—without the headache of scattered cloud services or complicated manual configurations.
Get started by running the stack in Docker, dive into the user flows, check out the monitoring dashboards, and push the system to its limits. The combination of a feature-rich frontend, robust backend, async messaging, database, and local language-model integration ensures there’s always more to discover.
If you’re looking to take your skills even further, try extending this base environment with additional microservices or custom test frameworks. The sky’s the limit with a self-contained local stack that you can tweak, break, and fix at will. Happy testing!
Tags: Testing
Categories: Testing
Updated:
